Magnetic sensors are used for the detection of positions without contact or wear and tear in control technology. They come into their own where inductive sensors reach their limits.
Magnetic sensors offer small designs with very long sensing ranges. Depending on the orientation of the magnetic field the sensor can be damped from the front or from the side.
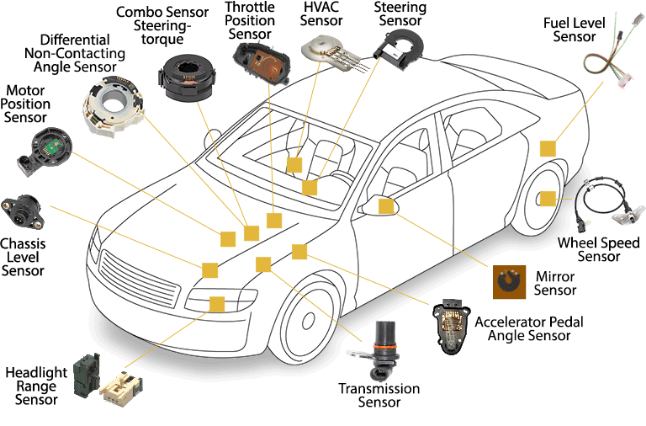
Sensor technologies for automotive applications:
position sensor
pressure sensor
temperature sensor
humidity sensor
fluid property sensor
acceleration sensor
……
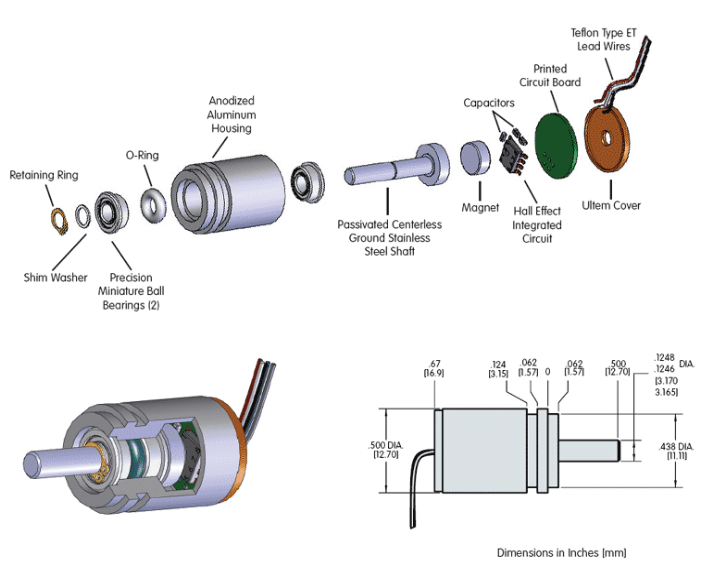
A Hall-effect speed or position sensor integrates a silicon chip with a Hall-effect sensing element and a signal processing circuit. Under the effect of a magnetic field created by a magnet inside the sensor or a magnetic target outside the sensor, the chip generates an electrical signal that can be used to measure speed or position
Speed sensors deliver electrical pulses at each passage of gear teeth or magnetic targets, induced by the alternating north/south magnetic poles.
Position sensors generally deliver a signal that varies continuously with the position of a moving metal or magnetic part.
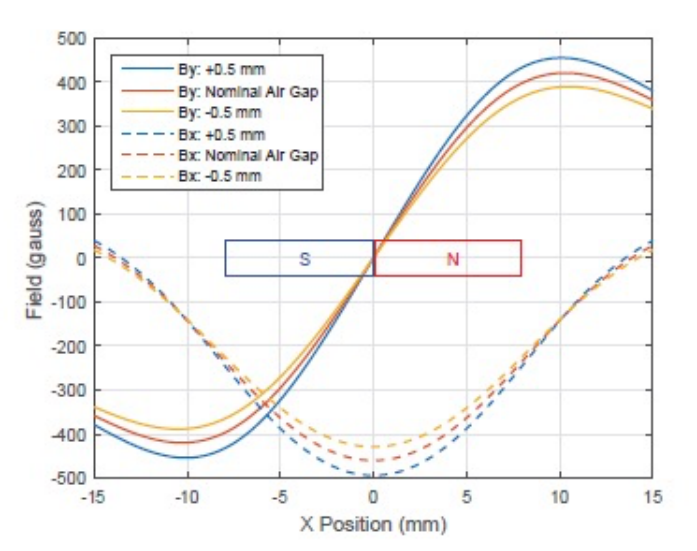
Characteristics (magnetic application):
Of all types and grades of magnets including sintered NdFeB, bonded NdFeB, Sintered SmCo, cast AlNiCo, sintered AlNiCo, hard ferrite, soft ferrite, bonded ferrite, FeCrCo, can be found in various sensors due to its wide applications in all classes of automobiles, cars, vans, buses, trucks, etc.
Generally, the higher class the car, the more sensors and the more magnets applied.
Testing: (cam sensor magnet as an example)
Surface gauss and flux density are 2 major measurement references.
Magnetic property:
Demagnetization curves in room temperature and designated high temperature
Supporting Equipment: Hysteresisgraph
Applicable magnet types: NdFeB magnets, SmCo magnets, hard ferrites
Irreversible demagnetization by comparing
Magnetic flux in room temperature
Magnetic flux after magnets are heated in elevated temperature
Supporting Equipment: flux meter, industrial oven
Applicable magnet types: NdFeB magnets, SmCo magnets, hard ferrite magnets.
Magnetic Deviation Angle
Like the Earth, every magnet is born with declination or variation. It's the angle on the horizontal plane between magnetic north and the designed north (perp to the plane).
Of all the magnet manufacturing processes, molding, pressing, machining (grinding, wire cutting or slicing) could assert great influence to the declination of a magnet.
In sensors, this figure can be of great assistance to design engineers to work out the perfect magnet for their applications.
Supporting Equipment: Magnetization Angle Tester
Appearance and dimensions
A.Appearance:
Salt Spray Test: set in certain humidity, PH based on application
Press Cook Test: set in air pressure, temperature and humidity based on application.
Plating/Coating thickness; using x-ray-fluorescence to analyze the thickness of surface plating/coating.
Supporting Equipment: SST Cabinet; PCT cabinet; XRF analyzer,
Applicable Magnet types: NdFeB magnets, SmCo magnets, hard ferrite magnets.
B.Dimensions:
1.Geometric tolerances (critical features, e.g. parallelism, perpendicularity, etc)
2.Desired size and shape
Supporting Equipment: micrometer, caliper, image measurement tool, CMM (Coordinate Measurement Machine)
Applicable Magnet types: NdFeB, SmCo, hard ferrite magnets.