Soft magnetic
- Share
- Issue Time
- Feb 18,2021
Summary
Magnetic material with low coercivity and high permeability. Soft magnetic materials are easy to magnetize and demagnetize, and are widely used in electrical and electronic equipment.

1.The development history of soft magnetic
Development History:The application of soft magnetic materials in industry began at the end of the 19th century. With the rise of electric power and telecommunications technology, low-carbon steel has been used to manufacture motors and transformers, and fine iron powder, iron oxide, and fine iron wire are used in the magnetic core of the inductor coil in the telephone line.
By the beginning of the 20th century, silicon steel sheets were developed to replace low-carbon steel, which improved the efficiency of transformers and reduced losses. Until now, silicon steel sheet still ranks first in the soft magnetic materials used in the power industry.
By the 1920s, the rise of radio technology promoted the development of high-permeability materials, and permalloy and permalloy magnetic powder cores appeared.
From the 1940s to the 1960s, the period of rapid development of science and technology, radar, television broadcasting, the invention of integrated circuits, etc., have higher requirements for soft magnetic materials, and produced soft magnetic alloy ribbons and soft ferrite materials. .
In the 1970s, with the development of telecommunications, automatic control, and computer industries, soft magnetic alloys for magnetic heads were developed. In addition to the traditional crystalline soft magnetic alloys, another type of material-amorphous soft magnetic has emerged. alloy.


2.Types of commonly used soft magnetic cores
Three ferromagnetic elements, iron, cobalt, and nickel, are the basic components of magnetic materials.
According to (main ingredients, magnetic characteristics, structural characteristics) product form classification:
1). Alloys: silicon steel sheet, permalloy, amorphous and nanocrystalline alloys
2). Powder core: magnetic powder core, including: iron powder core, sendust core, high magnetic flux powder core (High+Flux), permalloy powder core (MPP)
3). Ferrites: special powder cores, including: manganese zinc series, nickel zinc series
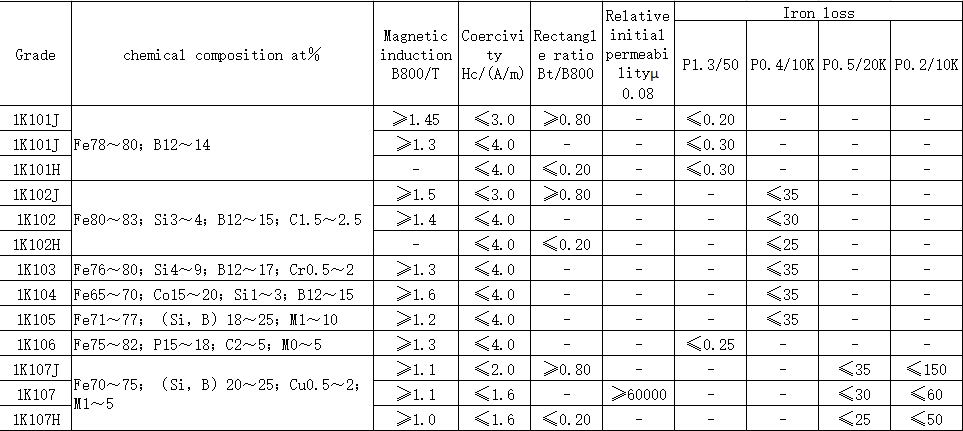
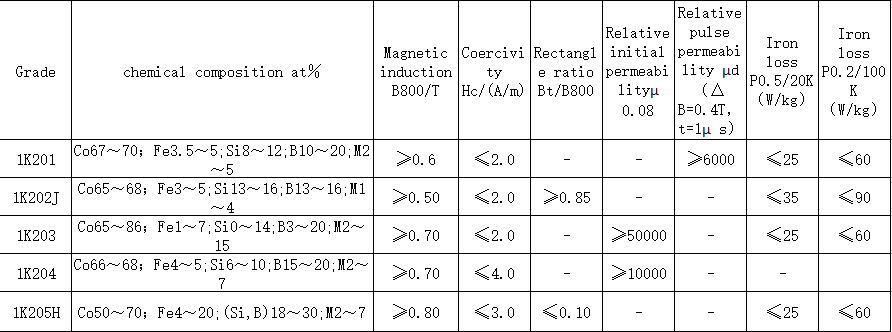
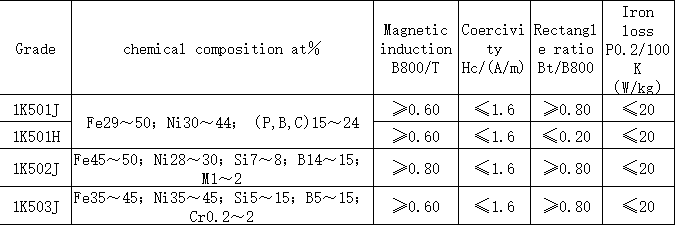
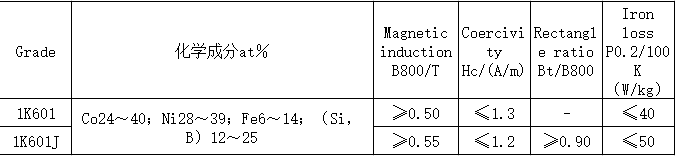
Electronic devices are increasingly developing in the direction of miniaturization, high performance, and high speed. Therefore, new requirements are put forward for high frequency inductance components, and further requirements are required to improve and enhance the performance of ferrite cores as inductance components. The requirements for magnetic core components are even higher. Good soft magnetic materials should meet the following basic requirements:
(1) In order to improve the functional efficiency, the initial permeability and maximum permeability should be high;
(2) In order to save resources, be light, thin and short, and quickly respond to the polarity reversal of the external magnetic field, the residual magnetic flux density should be low and the saturation magnetic induction should be high;
(3) Low loss, improve functional efficiency;
(4) The coercivity is small, and the high frequency magnetic performance is improved;
(5) High resistivity, improve high frequency performance and reduce eddy current loss;
(6) Low magnetostriction coefficient, reducing noise;
(7) The magnetic anisotropy coefficient K, which is the basic characteristic, should be low, and it is easy to magnetize in all crystal directions.
From the changes in the production of soft magnetic materials in various countries in recent years, it can be seen that the world's production pattern of soft magnetic materials has undergone great changes. There will still be a substantial increase in output, but competition will become more intense. Therefore, how to reduce costs, improve efficiency, improve product quality and market competitiveness will become the key to competition.
In short, the development of soft magnetic materials will develop in the direction of high saturation magnetic induction, high permeability, high Curie temperature, low loss, low coercivity, high frequency, miniaturization, and thin profile. The soft ferrite material is further developed to high frequency, high permeability and low loss. Amorphous and nanocrystalline soft magnetic alloys will develop new and functional amorphous and nanocrystalline composite materials to broaden the application fields of amorphous and nanocrystalline composite materials.