Rotors & Stators
- Share
- Issue Time
- Jan 22,2021
Summary
Motor refers to an electromagnetic device that realizes the conversion or transmission of electric energy according to the law of electromagnetic induction.
The motor is represented by the letter M in the circuit. Its main function is to generate driving torque. As a power source for electrical appliances or various machinery, the generator is represented by the letter G in the circuit. Its main function is to convert mechanical energy into Electricity
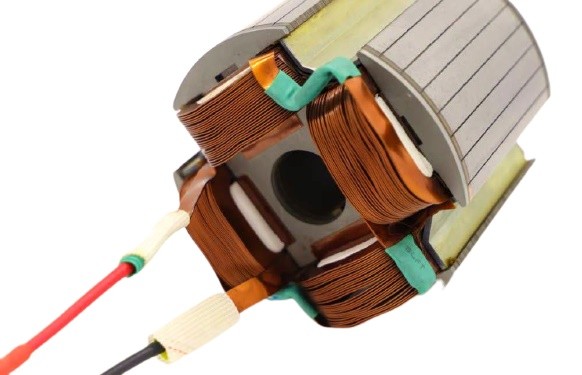
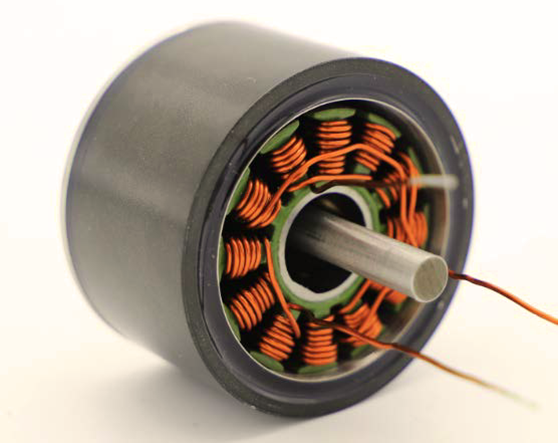
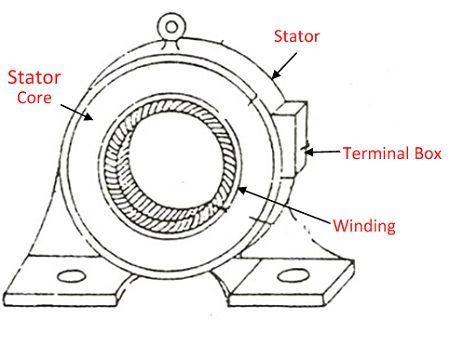
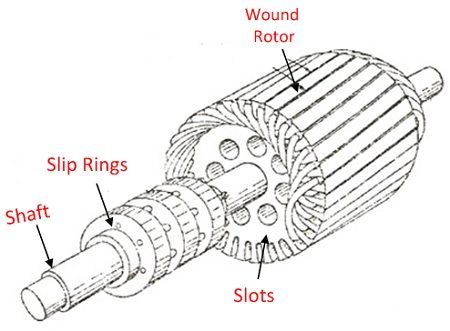
| Basis for Comparison | Stator | Rotor |
| Definition | It is a stationary part of the machine | It is the rotating part of the motor. |
| Parts | Outer frame, stator core and stator winding. | Rotor winding and Rotor core |
| Supply | Three-phase Supply | DC supply |
| Winding Arrangement | Complex | Easy |
| Insulation | Heavy | Less |
| Friction Loss | High | Low |
| Cooling | Easy | Difficult |

Silicon steel laminator

Power Tool

2000 rpm, 138 N·m



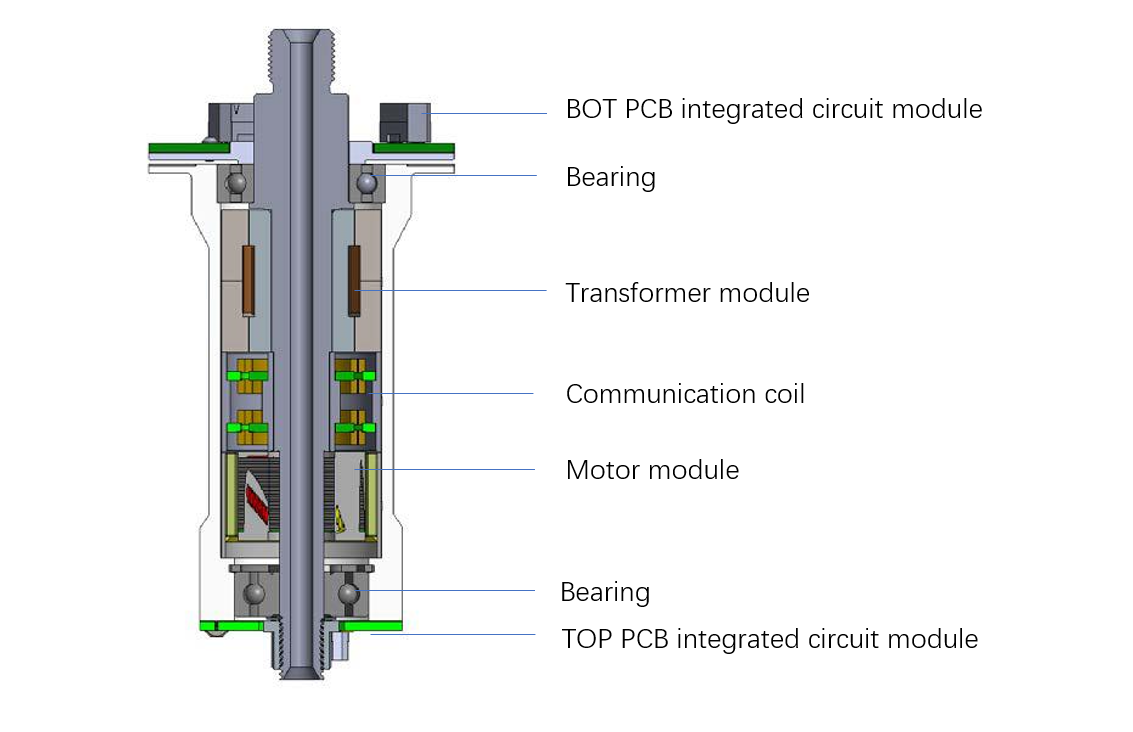
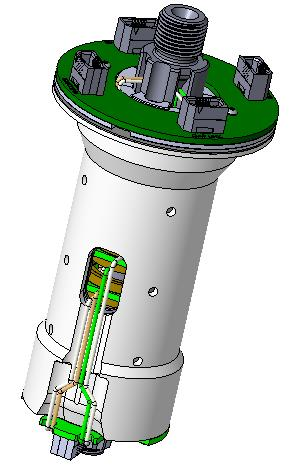
|
Laser channels: 128 Scanning distance: 300m Working tolerance: ±3cm Power: 26W RPM: 600±3rpm or 1200±10rpm Water proof level:IP67 Load: 1.75Kg Rotor moment of inertia(at 1.75 kg mass): 5500kg*mm² Transformer spec: 5V +/- 3%, 1:1, 5uH +/- 10 Data rate: 1Gbps. Max |
||



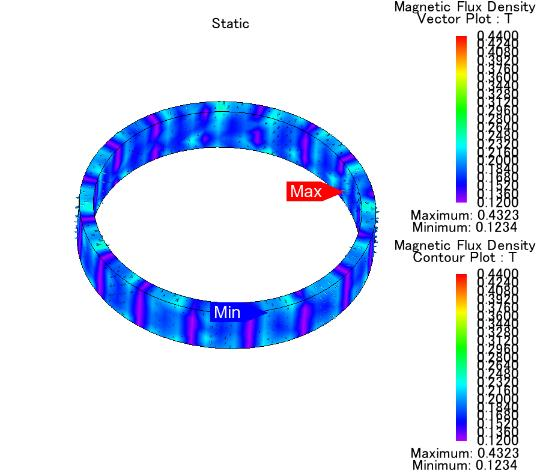



|
Magnetic Specs ‒ Material:Isotropic Pressing NdFeB Magnet ‒ Process: Pressing forming ‒ Magnet dimensions are stably controlled within 0.02mm ‒ High consistency of strength and density ‒ Density: ≥6.1g/cm3 ‒ Extreme wide deviation ±0.5° in different batches ‒ Peak deviation of magnetic poles is less than 3% |
||


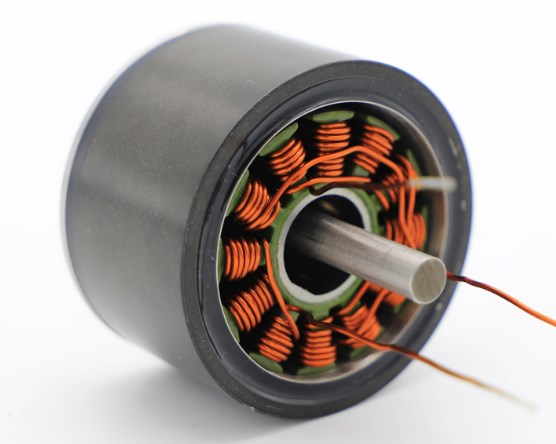

|
‒ Max thrust (16V):4.1kgf ‒ Max thrust(20V) :5.05kgf ‒ Max power:645W ‒ Power:26W ‒ Weight in water:156g |
||






Conclusion
The static part of the machine is known stator. And the rotating part of the machine is known as the rotor.
The rotor is placed inside the core of the stator. The three-phase is supplied to the stator winding which produces the rotating magnetic field. The rotor rotates inside the rotating magnetic field.
Thus, an emf is induced because of the interaction of magnetic field of rotor and stator.
For technical discussion and inquries, feel free to contact us at info@vectormagnets.com or find us here.