Traction motors in electric vehicles
- Share
- Issue Time
- Oct 22,2020
Summary
New energy vehicles refer to the use of unconventional vehicle fuels as the power source (or the use of conventional vehicle fuels, the use of new on-board power devices), the integration of advanced technologies in vehicle power control and driving, and the formation of advanced technical principles and Cars with new technology and new structure.
1. What is new energy vehicles?
New energy vehicles refer to the use of unconventional vehicle fuels as the power source (or the use of conventional vehicle fuels, the use of new on-board power devices), the integration of advanced technologies in vehicle power control and driving, and the formation of advanced technical principles and Cars with new technology and new structure.
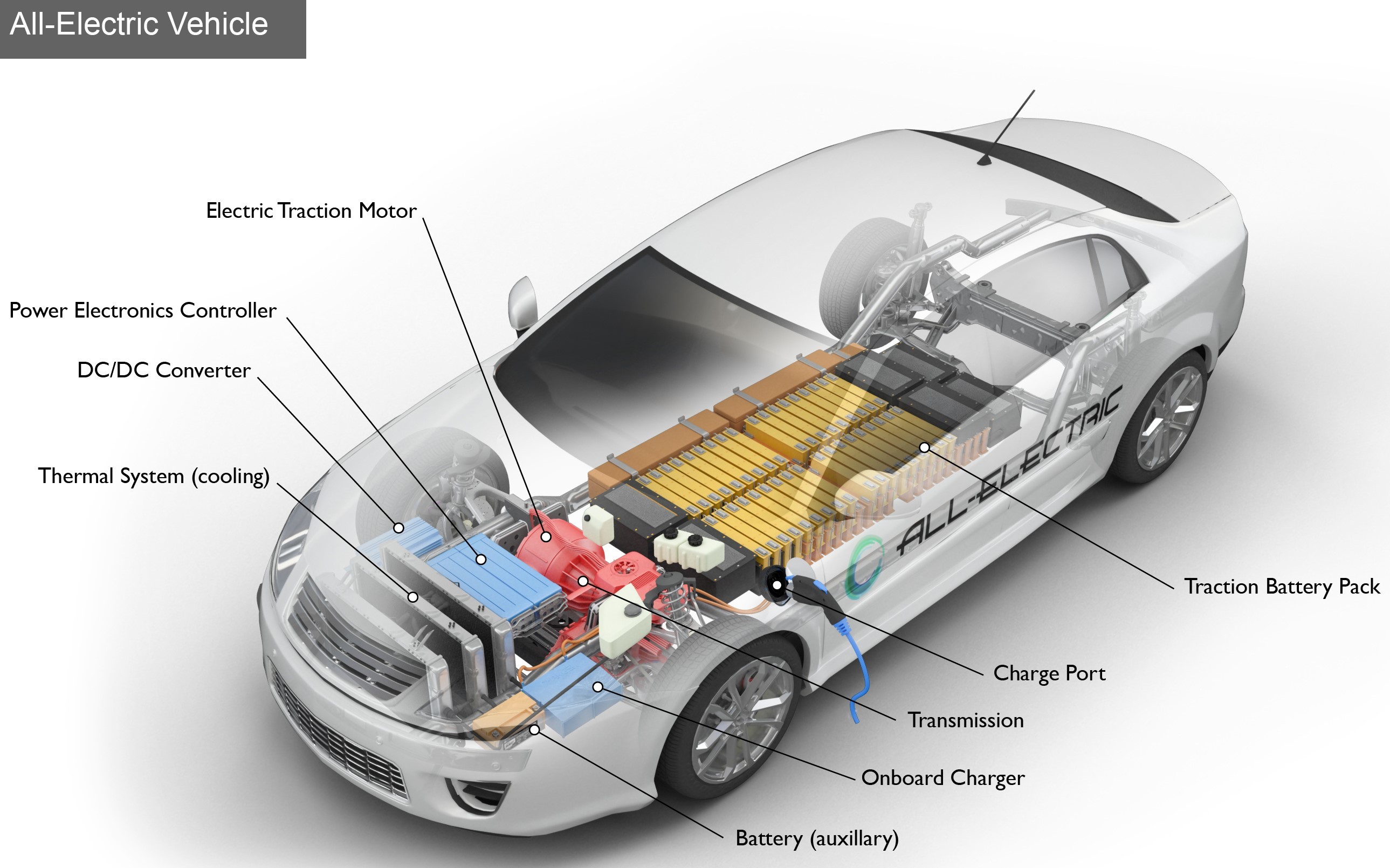
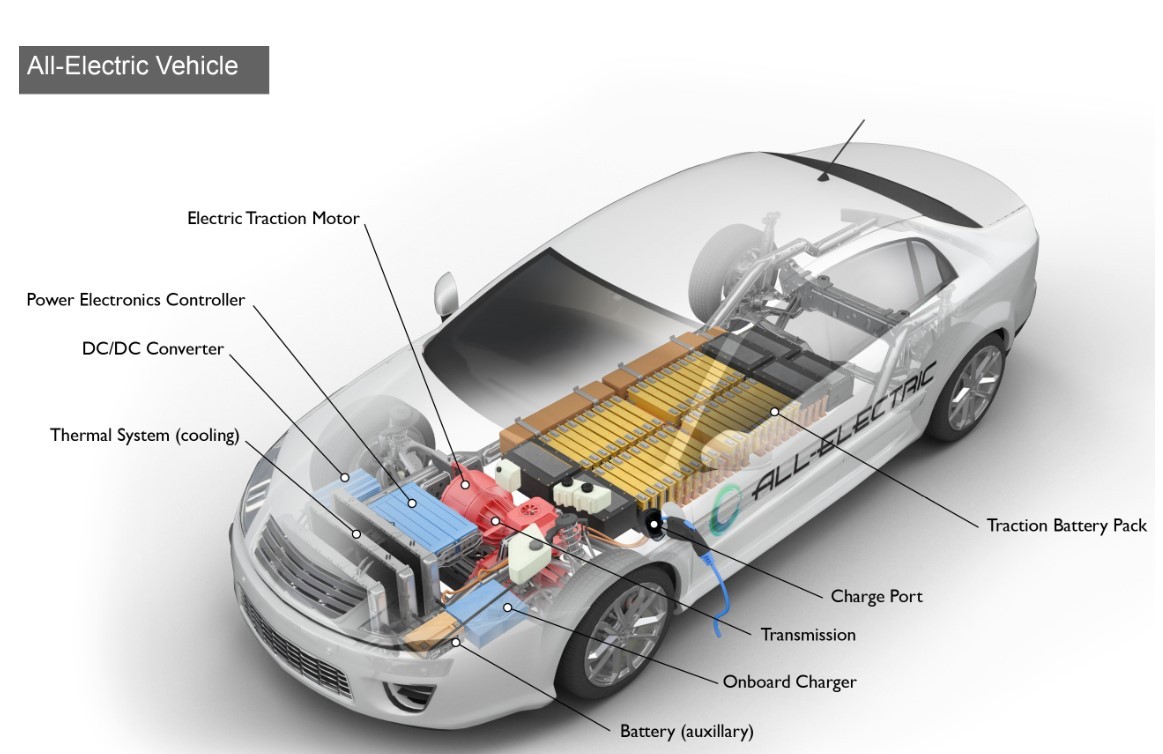
2. Composition of new energy vehicles
Battery (all-electric auxiliary)
In an electric drive vehicle, the auxiliary battery provides electricity to power vehicle accessories.
Charge port
The charge port allows the vehicle to connect to an external power supply in order to charge the traction battery pack.
DC/DC converter
This device converts higher-voltage DC power from the traction battery pack to the lower-voltage DC power needed to run vehicle accessories and recharge the auxiliary battery.
Electric traction motor
Using power from the traction battery pack, this motor drives the vehicle's wheels. Some vehicles use motor generators that perform both the drive and regeneration functions.
Onboard charger
Takes the incoming AC electricity supplied via the charge port and converts it to DC power for charging the traction battery. It monitors battery characteristics such as voltage, current, temperature, and state of charge while charging the pack.
Power electronics controller
This unit manages the flow of electrical energy delivered by the traction battery, controlling the speed of the electric traction motor and the torque it produces.
Thermal system (cooling)
This system maintains a proper operating temperature range of the engine, electric motor, power electronics, and other components.
Traction battery pack
Stores electricity for use by the electric traction motor.
Transmission (electric): The transmission transfers mechanical power from the electric traction motor to drive the wheels.
3. The motor drive system
The motor drive system of new energy vehicles is one of the three core components of new energy vehicles.
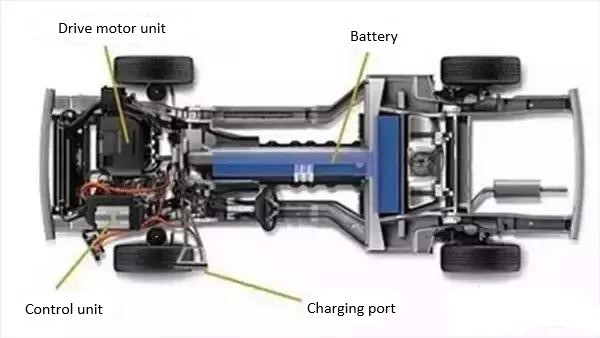
In simple terms, the motor drive system is mainly composed of two parts: the drive motor and the motor controller. Among them, the upstream of the motor industry chain is the supplier of raw materials such as electrolytic copper (magnet wire), silicon steel, steel, aluminum, insulating materials, and permanent magnet materials, as well as the supplier of accessories such as bearings and coolers, and the downstream is the vehicle factory.
4. Four types of drive motors
At present, the commonly used drive motors for new energy vehicles mainly include DC motors, AC asynchronous motors, permanent magnet synchronous motors and switched reluctance motors.
From the perspective of the application of different types of new energy vehicle drive motors in China, the current AC asynchronous induction motors and switched reluctance motors are mainly used in new energy commercial vehicles, especially new energy buses, and the actual assembly applications of switched reluctance motors are rare; Magnetic synchronous motors are mainly used in new energy passenger cars.
Performance and type |
DC |
Asynchronous motor |
Permanent magnet synchronous motor |
Switched magnetic group motor |
Power density |
low |
medium |
high |
Higher |
Range of rotation/rpm |
4000-6000 |
12000-20000 |
4000-10000 |
>15000 |
Weight |
heavy |
medium |
light |
light |
Volume | big | medium | small | small |
Reliability | bad | good | general | good |
Structural robustness | bad | good | good | good |
Controller cost | low | high | high | general |
Application situation | Eliminated | Currently mainly Tesla applications | Wide range of applications | Currently in the fields of electric buses, household appliances, etc. |
Advantage | Low cost, easy to control, etc. | Simple structure, good reliability, easy control of cost | High efficiency, simple structure, small size, etc. | Simple and robust structure, high reliability and low cost |
Disadvantage | Complex structure, low speed, large volume, frequent maintenance | Low efficiency, poor speed regulation | Higher cost, magnetic decay at high temperature | Large torque fluctuation and high noise |
Motor type |
DC brush motor |
Permanent magnet motor |
AC induction motor |
Switched magnetic group motor |
Highest efficiency(%) | 85-89 | 90-97 | 94-95 | 90 |
10%Load failure rate(%) | 80-87 | 90-92 | 79-85 | 78-86 |
Maximum speed(r/min) | 4000-6000 | 4000-10000 | 9000-15000 | <15000 |
Comparison of relative cost per unit output power |
1 |
1-1.5 |
0.8-1.2 |
0.6-1 |
Controller relative price comparison |
1 |
2.5 |
3.5 |
4.5 |
Robust and reliable |
good |
good |
excellent |
excellent |