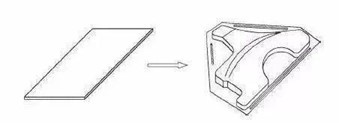
More than a dozen stamping and drawing processes, how much do you know?
- Share
- Issue Time
- Feb 28,2024
Stretch forming is a stamping processing
method that uses a mold to form a flat blank into an open hollow part. As one
of the main stamping processes, drawing is widely used. Thin-walled parts with
cylindrical, rectangular, stepped shapes, spherical, tapered, parabolic and
other irregular shapes can be made by the drawing process, and more complex
parts can also be manufactured if combined with other stamping and forming processes.

The use of stamping equipment for the
stretching and forming of products, including: drawing, redrawing, reverse
drawing, thinning and drawing.
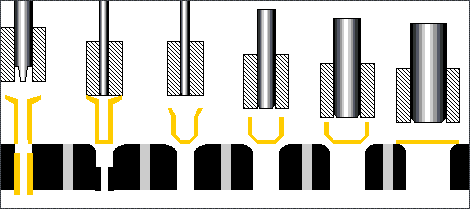
Stretching process: Using the pressing plate device, using
the punching force of the punch, part or all of the flat plate is pulled into
the cavity of the concave mold and shaped into a container with a bottom.
Stretching of the side wall of the container parallel to the direction of
stretching is a simple stretching process, while stretching of conical (or
corner pyramid) containers, hemispherical containers, parabolic containers,
etc., also includes expansion processing.
Re-drawing process: that is, for the deep-drawn products that
cannot be completed by one stretching process, the formed products that are
stretched again need to be stretched to increase the depth of the shaped
container.
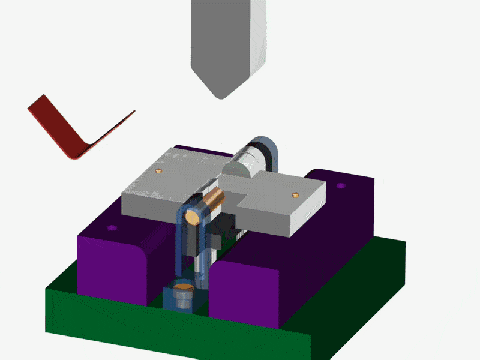
Reverse drawing machining: This is a process in which the stretched
workpiece of the previous process is reversed stretched, and the inside of the
workpiece becomes the outside, and the outer diameter is reduced.
Thinning and stretching processing: the formed container is squeezed into the
concave mold cavity slightly smaller than the outer diameter of the container
with punch, so that the outer diameter of the container with a bottom becomes
smaller, and the wall thickness becomes thinner, which not only eliminates the
deviation of wall thickness, but also makes the surface of the container
smooth.
When using stamping equipment for metal
stamping and drawing processing, the following 16 types are included:
01 Round drawing
Stretching of products with flanged
(flanged) cylinders. The flange and the bottom are both plane shaped, the side
wall of the cylinder is axisymmetric, and the deformation is evenly distributed
in the same circumference, and the blank on the flange produces drawing
deformation.
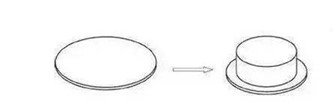
02 Ellipse drawing
The deformation of the blank on the
flange is tensile deformation, but the amount of deformation and the
deformation ratio change accordingly along the shape of the profile. The
greater the curvature, the greater the plastic deformation of the blank, and
conversely, the smaller the curvature, the smaller the plastic deformation of
the blank.

03 Rectangular drawing
A low-rectangular part that is formed by
a single stretch. When stretched, the tensile resistance at the fillet of the
flange deformation zone is greater than that at the straight edge, and the
degree of deformation at the fillet is greater than that at the straight edge.
04 Hill drawing
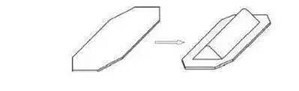
05 Hill drawing
The blank deformation in the forming
process of the mound cover plate is not a simple tensile deformation, but a
composite forming with both tensile and bulging deformation. The deformation of
the blank on the pressing surface is tensile (tensile stress in the radial
direction and compressive stress in the tangential direction), while the
deformation of the blank inside the contour (especially in the central area) is
a swelling deformation (both radial and tangential tensile stresses).
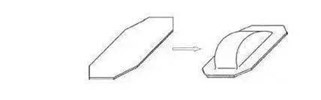
06 With flange hemisphere drawing
When the spherical part is stretched,
the blank is in partial contact with the spherical top of the punch, and most
of the rest is in an unconstrained free state suspended in the air. Therefore,
the main process problem of the stretching of such spherical parts lies in the
severe thinning of the local contact part, or the instability and wrinkling of
the curved part.
07 Flange drawing
The flange part of the stretched product
is processed by shallow drawing. The stress-strain profile is similar to that
of a compression flange. Due to the tangential compressive stress, it is easy
to wrinkle, so the forming limit is mainly limited by compression wrinkling.
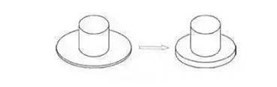
08 Flange drawing
The flange part of the pre-process
stretched product is angled and restretched, which requires the material to
have good plasticity.
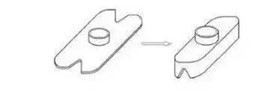
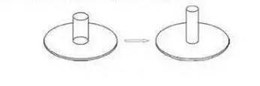
09 Deep drawing
Stretching products that exceed the
drawing limit need to be stretched more than twice before they can be
completed. Products that have been stretched in the depth direction of the
former station are redrawn in the depth direction. Wide-flange stretches are
stretched to the required flange diameter for the first stretch and remain the
same when they are then stretched.
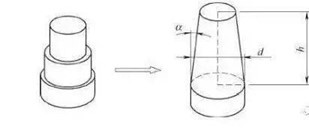
10 Taper drawing
H/d>0.8, α=10 ° ~ 30 ° deep conical
parts, due to the large depth, the degree of deformation of the blank is
larger, only rely on the local area of the blank and punch contact to transmit
the forming force, it is easy to cause the blank to be over-thinned and even
cracked, and it needs to be gradually formed after many transitions. The
stepped stretching method is to first stretch the blank into a stepped
transition, the stepped shape is tangent to the inner shape of the tapered
part, and finally form a tapered shape. The number of stretching times and
process of the stepped transition piece are the same as the stretching of the
stepped cylindrical piece.
11 Rectangular redrawing
The deformation of a highly rectangular
part formed by multiple stretches is not only different from that of a deep
cylindrical part, but also from that of a low box-shaped part. The picture
shows that when the multi-station automatic conveyor press is processed for
high rectangular boxes, the shape and size of the parts change with the
stretching height during the multiple stretching process.
12 Surface forming
The surface is stretched and formed, so
that the outer flange part of the metal flat blank is reduced, and the inner
flange part is elongated, and it becomes a stamping and forming method for
hollow products with a curved surface shape of non-straight wall and non-flat
bottom.
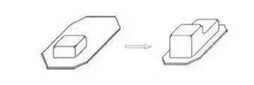
13 Step drawing
The left primary drawn product is
redrawn and formed into a stepped bottom on the right. The deeper parts are
deformed at the beginning of the stretch form, and the shallower parts are
deformed at the later stage of the stretch. The sidewall of the changing part
of the step is prone to induce shear stress and deformation.
14 Reverse drawing
The workpiece that is stretched in the
previous process is reversed and re-stretched. The reverse tensile method can
increase the radial tensile stress, which can be better for preventing
wrinkling. It is also possible to increase the stretch coefficient of
restretching.
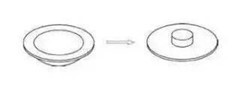
15 Ironing
Different from ordinary stretching,
thinning stretching mainly changes the thickness of the cylinder wall of the stretched
part during the stretching process. The gap between the convex and concave dies
is less than the thickness of the blank, and the straight-walled part of the
blank is under the greater uniform compressive stress when passing through the
gap, and the wall thickness becomes thinner during the stretching process,
while eliminating the deviation of the wall thickness of the container,
increasing the smoothness of the surface of the container, and improving the
accuracy and strength.
16 Panel drawing
Panel products are sheet stamping parts
with complex surface shapes. In the drawing process, the deformation of the
blank is complex, and its forming properties are no longer simple stretch
forming, but compound forming with deep drawing and expansion at the same time.